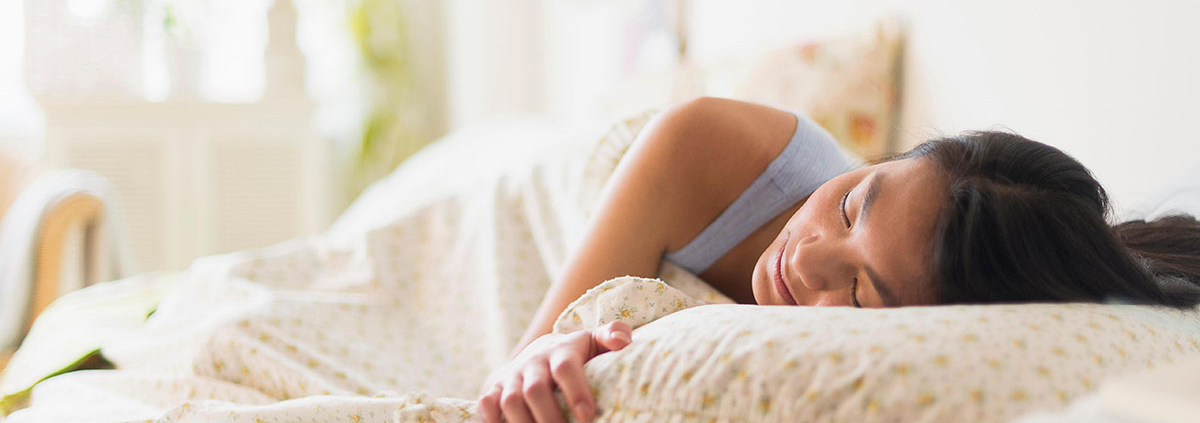
Disrupted sleep is linked to increased risk of death, particularly in women
For the first time, a study has shown a clear link between the frequency and duration of unconscious wakefulness during night-time sleep and an increased risk of dying from diseases of the heart and blood vessels, and death from any cause, particularly in women.
The study of 8001 men and women, which is published in the European Heart Journal, found that women who experienced unconscious wakefulness most often and for longer periods of time had nearly double the risk of dying from cardiovascular disease during an average of between 6 and 11 years’ follow-up, when compared to the risk in general female population. The association was less clear in men, and their risk of cardiovascular death increased by just over a quarter compared to the general male population.
Unconscious wakefulness, also known as cortical arousal, is a normal part of sleep. It occurs spontaneously and is part of the body’s ability to respond to potentially dangerous situations, such as noise or breathing becoming obstructed. Pain, limb movements, trauma, temperature and light can also be triggers.
Release date: 20 April 2021
Source: European Society of Cardiology