What is Parkinson Disease (PD)?
- Parkinson disease (PD) is caused by a disruption
 of dopaminergic neurotransmission in the basal ganglia and development of eosinophilic inclusions (Lewy bodies) in the residual neurons.
of dopaminergic neurotransmission in the basal ganglia and development of eosinophilic inclusions (Lewy bodies) in the residual neurons. - Genetic predisposition: May present; up to 15% of patients have a first- or second-degree relative with Parkinson disease.
- No clear environmental links to the disease identified.
Epidemiology
- In US
- Parkinson disease is the second most common progressive neurodegenerative disorder after Alzheimer disease.
- Parkinson affects about 1% of the population older than age 60 years
- 4% to 5% of those older than 85 years
- 4% to 5% of those older than 85 years
- In Australia
- Prevalence: 120–150 per 100 000
- Lifetime risk is 1 in 40
- Mean age of onset: Between 58 and 62 years.
Clinical Features
The hallmark clinical features of Parkinson disease (usually asymmetric onset) include
- Tremor
- Presenting symptom in up to 70% of patients.
- Asymmetric rest tremor is virtually pathognomonic of Parkinson disease.
- Differential Diagnosis: essential tremor
- Usually symmetric
- Exacerbated by action
- Rigidity: Cog wheeling quality during passive movement of the limb
- Bradykinesia:

- Refers to the slowness of movements
- Usually begins in an asymmetric fashion
- Described by the patient as “weakness” of an extremity
- Strength testing: Normal
- Difficulty with fine finger tasks
- Micrographia
- Paucity of facial expression (masked face)
- Lack of blinking
- Excessive salivation (late stages)
- Swallowing problems
- Soft, slow monotonous speech
Other clinical features associated with Parkinson disease include
- General presentations:
- Tiredness
- Lethargy
- Restlessness
- Trouble getting out of chair or car and turning over in bed
- Gait disorder
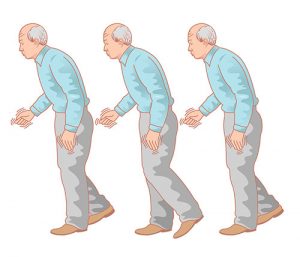
- Start hesitation
- Festination
- No arm swing on one or both sides
- Slow and narrow based gait
- Short steps (petit pas)
- Slow turning circle (‘turn by numbers’)
- ‘Freezing’ when approaching an obstacle
- Poor balance
- Posture
- Progressive forward flexion of trunk (stooped)
- Flexion of elbow at affected side
- Autonomic symptoms
- Constipation: common
- Postural hypotension: may be induced by treatment

- Neuropsychiatric
- Depression (early stages)
- Anxiety
- Sleep disorder
- Progressive dementia in 30–40% usually after 10 years.
- Hallucinations
- Reduced sense of smell: One of the first symptoms
- Think of PD in an older person presenting with falls
Diagnosis
- Based on the history and examination (it is a clinical diagnosis)
- There is no laboratory test for PD
- Differential diagnosis include hypothyroidism and depression
- Drug-induced Parkinsonism:
- Common drugs: phenothiazines, butyrophenones and reserpine.
- Tremor is uncommon
- Rigidity and bradykinesia may be severe.
Management

- Pharmacotherapy
- Surgical treatment
- Treatment of Non-motor Symptoms