What are Electrodiagnostic aids?
Electrodiagnostic aids provide valuable information about the nervous system and usually considered as extensions of medical history and physical examination.
FAQ
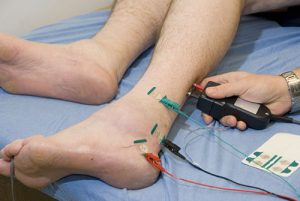
What is EMG / NCS? Why it is done?
Including:
Nerve conduction studies. (NCS)
– Latency
– Amplitude
– Velocity (NCV)
– F waves
– H reflexes
Electromyography (EMG)
Evoked potentials
– Visual evoked potentials (VEP)
– Brainstem auditory evoked potentials (BAEP)
– Short latency evoked potentials (SSEP)
Electroencephalography
Asked For clients complains of
- Paresthesia (numbness, tingling,… in hands or feet)
- Neck or back pain (specially when radiated to limbs)
- Weakness
- Gait disturbances, intermittent claudication
- Blurred vision
- Seizure
clinical utility: Helpful in different group of diseases
- Radiculopathy
- Polyneuropathy: Such as patients with diabetes, renal failures, thyroid problems, addicted suspected for lead poisoning, history of chemotherapy, infectious disease (HIV, HTLV1), AIDP (Guillain-Barre syndrome), rheumatologic disorders (Rheumatoid arthritis, Lupus…)
- Entrapment neuropathy: Most common type is carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS)
- Myopathy
- Motor neuron disease: Most important Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS)
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS): VEP is indicated